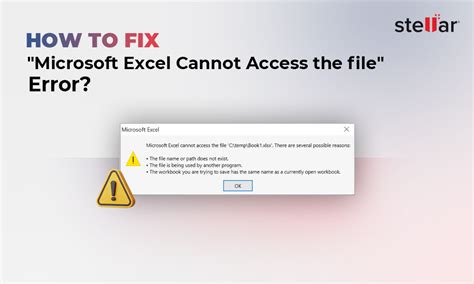
Introduction to Excel Error Fixes
Excel is a powerful tool used for data analysis, calculations, and visualization. However, like any other software, it is not immune to errors. These errors can range from simple formula mistakes to complex issues that require a deeper understanding of the program. In this article, we will explore five common Excel errors and their fixes, helping you to overcome obstacles and work more efficiently in Excel.
Understanding Excel Errors

Before we dive into the fixes, it’s essential to understand the nature of Excel errors. These errors can be categorized into several types, including: - Syntax Errors: These occur when a formula is not correctly formatted. - Runtime Errors: These happen during the execution of a formula or function. - Logic Errors: These are errors in the logic of a formula or function, leading to incorrect results. - System Errors: These are errors caused by the system or environment in which Excel is running.
Fix 1: Resolving the #VALUE! Error

The #VALUE! error occurs when a value is not a number or when a function or formula is used incorrectly. To resolve this error: - Check the formula for any syntax errors. - Ensure that all arguments are correctly entered. - Verify that the function or formula is appropriate for the data type being used. -
📝 Note: Sometimes, using the VALUE function can help convert text to numbers, but use it with caution as it may lead to errors if not used correctly.
Fix 2: Dealing with the #REF! Error

The #REF! error appears when a reference to a cell is invalid. This can happen if the referenced cell has been deleted or if the formula is referencing a cell outside the current worksheet or workbook. To fix this: - Check if the referenced cell exists and is correctly identified. - If the cell has been deleted, either restore it or update the formula to reference an existing cell. - Use named ranges or absolute references to minimize the risk of reference errors. - Consider using the IFERROR function to handle and manage reference errors more gracefully.
Fix 3: Solving the #DIV/0! Error

The #DIV/0! error occurs when a formula attempts to divide by zero. To resolve this: - Check the formula for any instances of division. - Ensure that the divisor (the number by which we are dividing) is not zero. - Use the IF function to check if the divisor is zero before performing the division. - Consider using the IFERROR function to return a custom value when a division by zero error occurs.
Fix 4: Handling the #N/A Error
The #N/A error is returned when a value is not available. This often happens with lookup functions like VLOOKUP or INDEX/MATCH. To fix this: - Verify that the lookup value exists in the lookup range. - Check for spelling mistakes or extra spaces in the lookup value or the lookup range. - Use the IFERROR function to handle #N/A errors and return a meaningful value instead. - Consider using the IFNA function, specifically designed to handle #N/A errors in newer versions of Excel.
Fix 5: Troubleshooting the #NAME? Error

The #NAME? error occurs when Excel does not recognize a name or a function in a formula. To resolve this: - Check the formula for spelling mistakes, especially in function names. - Ensure that the function or name is correctly defined. - Use the Formula AutoComplete feature to help select functions and names correctly. -
💡 Note: If using a custom function or add-in, make sure it is installed and enabled in Excel.
Best Practices to Minimize Excel Errors
While fixing errors is crucial, preventing them from occurring in the first place is even more beneficial. Here are some best practices: - Double-check formulas: Before entering a formula, ensure you understand its components and how it works. - Use Excel’s built-in functions: Excel has a wide range of functions designed to perform specific tasks. Using these can reduce the likelihood of errors. - Test formulas: Always test a formula with sample data before applying it to your actual dataset. - Document your work: Keeping a record of your formulas and changes can help in troubleshooting and understanding how your spreadsheet works.
Utilizing Excel Tools for Error Detection
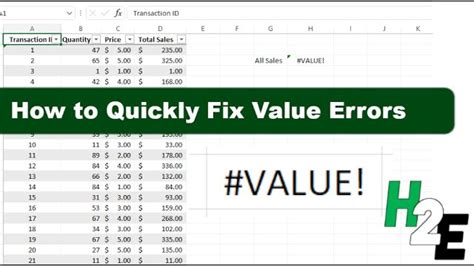
Excel offers several tools and features to help detect and fix errors: - Error Checking: Excel can automatically check for errors in formulas and provide suggestions for corrections. - Formula Auditing: Tools like Trace Precedents and Trace Dependents can help identify how formulas interact with each other. - Watch Window: This feature allows you to monitor the value of a cell and see how it changes as you make changes to the worksheet.
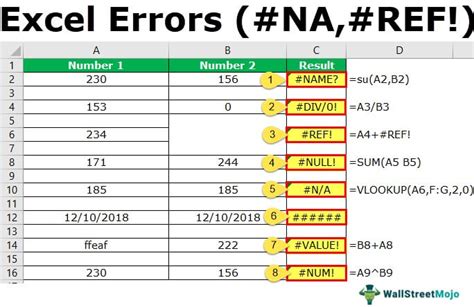
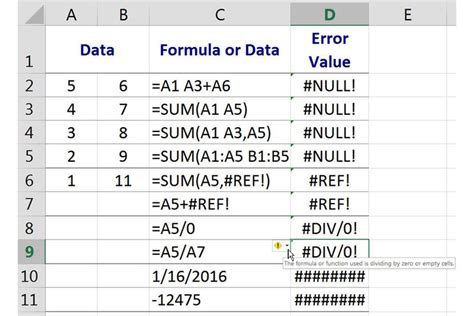
| Error Type | Description | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| #VALUE! | Incorrect value or formula syntax | Check syntax, ensure correct data type |
| #REF! | Invalid cell reference | Verify cell existence, use named ranges |
| #DIV/0! | Division by zero | Check divisor, use IF function |
| #N/A | Value not available | Verify lookup value, use IFERROR |
| #NAME? | Unrecognized name or function | Check spelling, ensure correct function usage |

In summary, Excel errors, though frustrating, can be managed and fixed with the right approach. By understanding the types of errors, applying best practices, and utilizing Excel’s built-in tools, you can efficiently troubleshoot and resolve errors, enhancing your productivity and accuracy in Excel.
What is the most common cause of the #VALUE! error in Excel?
+
The most common cause of the #VALUE! error is incorrect syntax or using a function or formula incorrectly with the wrong data type.
How can I prevent the #REF! error when referencing cells in Excel?

+
You can prevent the #REF! error by ensuring that the referenced cell exists and is correctly identified. Using named ranges or absolute references can also minimize the risk of reference errors.
What is the purpose of the IFERROR function in Excel?

+
The IFERROR function is used to catch and manage errors in formulas, allowing you to return a custom value instead of the error, thus making your spreadsheets more robust and user-friendly.