Introduction to Democracy

Democracy is a system of government where power is vested in the people, either directly or through elected representatives. The term democracy comes from the Greek words “demos,” meaning people, and “kratos,” meaning power. It is a form of government that allows citizens to participate in the decision-making process, either by voting for their representatives or by voting on laws and policies directly. Democracy is often considered the best form of government, as it provides citizens with the freedom to express their opinions and participate in the political process.
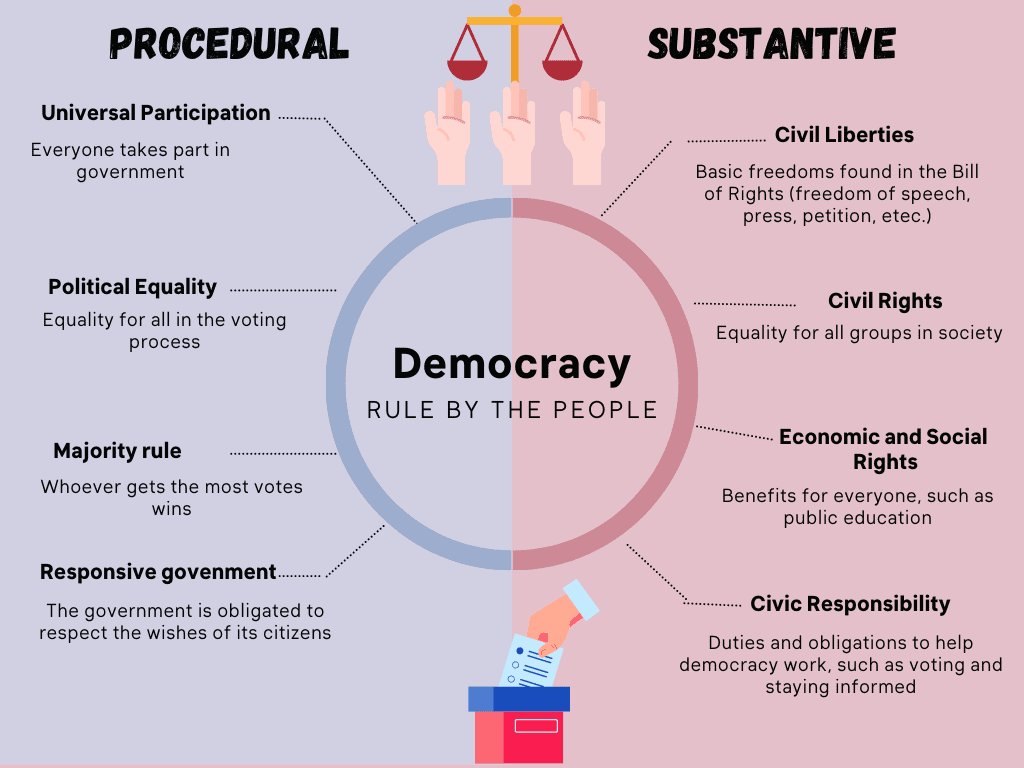
Key Principles of Democracy

There are several key principles that are essential to a democratic system of government. These include: * Free and fair elections: Citizens have the right to vote for their representatives and to participate in the electoral process. * Protection of individual rights: The government must protect the rights of all citizens, including the right to freedom of speech, freedom of assembly, and freedom of the press. * Separation of powers: The government is divided into separate branches, such as the executive, legislative, and judicial, to prevent any one branch from becoming too powerful. * Accountability: The government is accountable to the people, and citizens have the right to hold their representatives accountable for their actions. * Transparency: The government must be transparent in its decision-making process, and citizens have the right to access information about government activities.
Benefits of Democracy

There are several benefits to a democratic system of government. These include: * Protection of individual rights: Democracy provides citizens with the freedom to express their opinions and participate in the political process. * Promotion of economic growth: Democracy can promote economic growth by providing a stable and secure environment for businesses to operate. * Encouragement of innovation: Democracy can encourage innovation by providing citizens with the freedom to pursue their ideas and creativity. * Improvement of living standards: Democracy can improve living standards by providing citizens with access to education, healthcare, and other essential services. * Reducing poverty and inequality: Democracy can reduce poverty and inequality by providing citizens with equal access to opportunities and resources.
Challenges Facing Democracy

Despite its many benefits, democracy is not without its challenges. Some of the challenges facing democracy include: * Corruption: Corruption can undermine the democratic process by allowing individuals or groups to use their power and influence for personal gain. * Inequality: Inequality can undermine democracy by providing some citizens with more access to resources and opportunities than others. * Polarization: Polarization can undermine democracy by creating divisions between different groups and making it difficult to find common ground. * Disinformation: Disinformation can undermine democracy by providing citizens with false or misleading information, which can influence their opinions and decisions. * External threats: External threats, such as terrorism or foreign interference, can undermine democracy by creating instability and undermining the rule of law.
Strengthening Democracy

To strengthen democracy, it is essential to address the challenges facing it. Some ways to do this include: * Improving education and critical thinking: Improving education and critical thinking can help citizens to make informed decisions and to evaluate information critically. * Promoting transparency and accountability: Promoting transparency and accountability can help to prevent corruption and ensure that the government is accountable to the people. * Encouraging citizen participation: Encouraging citizen participation can help to ensure that all citizens have a voice in the democratic process. * Protecting individual rights: Protecting individual rights can help to ensure that all citizens are treated equally and have access to the same opportunities. * Addressing inequality: Addressing inequality can help to ensure that all citizens have access to the same resources and opportunities.
| Country | Form of Government | Level of Democracy |
|---|---|---|
| United States | Federal Republic | High |
| Canada | Parliamentary Democracy | High |
| United Kingdom | Parliamentary Democracy | High |
| China | One-Party State | Low |
| Russia | Federal Semi-Presidential Republic | Medium |

📝 Note: The level of democracy can vary depending on the source and the criteria used to evaluate it.
In summary, democracy is a system of government that provides citizens with the freedom to express their opinions and participate in the political process. While it has many benefits, it also faces several challenges, including corruption, inequality, polarization, disinformation, and external threats. To strengthen democracy, it is essential to address these challenges and promote transparency, accountability, citizen participation, and individual rights.
What is democracy?

+
Democracy is a system of government where power is vested in the people, either directly or through elected representatives.
What are the benefits of democracy?

+
The benefits of democracy include protection of individual rights, promotion of economic growth, encouragement of innovation, improvement of living standards, and reduction of poverty and inequality.
What are the challenges facing democracy?

+
The challenges facing democracy include corruption, inequality, polarization, disinformation, and external threats.